98 KiB
Chapter 3: A First Impression Of C++
In this chapter C++ is further explored. The possibility to declare functions in structs is illustrated in various examples; the concept of a class is introduced; casting is covered in detail; many new types are introduced and several important notational extensions to C are discussed.
3.1: Notable differences with C
Before we continue with the real object-approach to programming, we first introduce some notable differences with the C programming language: not mere differences between C and C++, but important syntactic constructs and keywords not found or differently used in C.
3.1.1: Using the keyword const
Even though the keyword const is part of the C grammar, its use is more important and much more common and strictly used in C++ than it is in C.
The const keyword is a modifier stating that the value of a variable or of an argument may not be modified. In the following example the intent is to change the value of a variable ival, which fails:
int main()
{
int const ival = 3; // a constant int
// initialized to 3
ival = 4; // assignment produces
// an error message
}
This example shows how ival may be initialized to a given value in its definition; attempts to change the value later (in an assignment) are not permitted.
Variables that are declared const can, in contrast to C, be used to specify the size of an array, as in the following example:
int const size = 20;
char buf[size]; // 20 chars big
Another use of the keyword const is seen in the declaration of pointers, e.g., in pointer-arguments. In the declaration
char const *buf;
buf is a pointer variable pointing to chars. Whatever is pointed to by buf may not be changed through buf: the chars are declared as const. The pointer buf itself however may be changed. A statement like *buf = 'a'; is therefore not allowed, while ++buf is.
In the declaration
char *const buf;
buf itself is a const pointer which may not be changed. Whatever chars are pointed to by buf may be changed at will.
Finally, the declaration
char const *const buf;
is also possible; here, neither the pointer nor what it points to may be changed.
The rule of thumb for the placement of the keyword const is the following: whatever occurs to the left to the keyword may not be changed.
Although simple, this rule of thumb is often used. For example, Bjarne Stroustrup states (in https://www.stroustrup.com/bs_faq2.html#constplacement):
Should I put
constbefore or after the type?I put it before, but that's a matter of taste.
const TandT constwere always (both) allowed and equivalent. For example:const int a = 1; // OK int const b = 2; // also OKMy guess is that using the first version will confuse fewer programmers (
is more idiomatic).
But we've already seen an example where applying this simple before placement rule for the keyword const produces unexpected (i.e., unwanted) results as we will shortly see (below). Furthermore, the idiomatic before-placement also conflicts with the notion of const functions, which we will encounter in section 7.7. With const functions the keyword const is also placed behind rather than before the name of the function.
The definition or declaration (either or not containing const) should always be read from the variable or function identifier back to the type identifier:
Buf is a const pointer to const characters
This rule of thumb is especially useful in cases where confusion may occur. In examples of C++ code published in other places one often encounters the reverse: const preceding what should not be altered. That this may result in sloppy code is indicated by our second example above:
char const *buf;
What must remain constant here? According to the sloppy interpretation, the pointer cannot be altered (as const precedes the pointer). In fact, the char values are the constant entities here, as becomes clear when we try to compile the following program:
int main()
{
char const *buf = "hello";
++buf; // accepted by the compiler
*buf = 'u'; // rejected by the compiler
}
Compilation fails on the statement *buf = 'u'; and not on the statement ++buf.
Marshall Cline's C++ FAQ gives the same rule (paragraph 18.5) , in a similar context:
[18.5] What's the difference between const Fred* p, Fred* const p and const Fred* const p?
You have to read pointer declarations right-to-left.
Marshall Cline's advice can be improved, though. Here's a recipe that will effortlessly dissect even the most complex declaration:
- start reading at the variable's name
- read as far as possible until you reach the end of the declaration or an (as yet unmatched) closing parenthesis.
- return to the point where you started reading, and read backwards until you reach the beginning of the declaration or a matching opening parenthesis.
- If you reached an opening parenthesis, continue at step 2 beyond the parenthesis where you previously stopped.
Let's apply this recipe to the following (by itself irrelevant) complex declaration. Little arrows indicate how far we should read at each step and the direction of the arrow indicates the reading direction:
char const *(* const (*(*ip)())[])[]
ip Start at the variable's name:
'ip' is
ip) Hitting a closing paren: revert
-->
(*ip) Find the matching open paren:
<- 'a pointer to'
(*ip)()) The next unmatched closing par:
--> 'a function (not expecting
arguments)'
(*(*ip)()) Find the matching open paren:
<- 'returning a pointer to'
(*(*ip)())[]) The next closing par:
--> 'an array of'
(* const (*(*ip)())[]) Find the matching open paren:
<-------- 'const pointers to'
(* const (*(*ip)())[])[] Read until the end:
-> 'an array of'
char const *(* const (*(*ip)())[])[] Read backwards what's left:
<----------- 'pointers to const chars'
Collecting all the parts, we get for char const *(* const (*(*ip)())[])[]: ip is a pointer to a function (not expecting arguments), returning a pointer to an array of const pointers to an array of pointers to const chars. This is what ip represents; the recipe can be used to parse any declaration you ever encounter.
3.1.2: Namespaces
C++ introduces the notion of a namespace: all symbols are defined in a larger context, called a namespace. Namespaces are used to avoid name conflicts that could arise when a programmer would like to define a function like sin operating on degrees, but does not want to lose the capability of using the standard sin function, operating on radians.
Namespaces are covered extensively in chapter [4]({{< relref "/docs/Name Spaces" >}}). For now it should be noted that most compilers require the explicit declaration of a standard namespace: std. So, unless otherwise indicated, it is stressed that all examples in the Annotations now implicitly use the
using namespace std;
declaration. So, if you actually intend to compile examples given in the C++ Annotations, make sure that the sources start with the above using declaration.
3.1.3: The scope resolution operator ::
C++ introduces several new operators, among which the scope resolution operator (::). This operator can be used in situations where a global variable exists having the same name as a local variable:
#include <stdio.h>
double counter = 50; // global variable
int main()
{
for (int counter = 1; // this refers to the
counter != 10; // local variable
++counter)
{
printf("%d\n",
::counter // global variable
/ // divided by
counter); // local variable
}
}
In the above program the scope operator is used to address a global variable instead of the local variable having the same name. In C++ the scope operator is used extensively, but it is seldom used to reach a global variable shadowed by an identically named local variable. Its main purpose is encountered in chapter 7.
3.1.4: cout, cin, and cerr
Analogous to C, C++ defines standard input and output streams which are available when a program is executed. The streams are:
cout, analogous tostdout,cin, analogous tostdin,cerr, analogous tostderr.
Syntactically these streams are not used as functions: instead, data are written to streams or read from them using the operators <<, called the insertion operator and >>, called the extraction operator. This is illustrated in the next example:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int ival;
char sval[30];
cout << "Enter a number:\n";
cin >> ival;
cout << "And now a string:\n";
cin >> sval;
cout << "The number is: " << ival << "\n"
"And the string is: " << sval << '\n';
}
This program reads a number and a string from the cin stream (usually the keyboard) and prints these data to cout. With respect to streams, please note:
- The standard streams are declared in the header file
iostream. In the examples in the C++ Annotations this header file is often not mentioned explicitly. Nonetheless, it must be included (either directly or indirectly) when these streams are used. Comparable to the use of theusing namespace std; clause, the reader is expected to #include with all the examples in which the standard streams are used. - The streams
cout,cinandcerrare variables of so-called class-types. Such variables are commonly called objects. Classes are discussed in detail in chapter 7 and are used extensively in C++. - The stream
cinextracts data from a stream and copies the extracted information to variables (e.g.,ivalin the above example) using the extraction operator (two consecutive>characters:>>). Later in the Annotations we will describe how operators in C++ can perform quite different actions than what they are defined to do by the language, as is the case here. Function overloading has already been mentioned. In C++ operators can also have multiple definitions, which is called operator overloading. - The operators which manipulate
cin,coutandcerr(i.e.,>>and<<)also manipulate variables of different types. In the above examplecout << ivalresults in the printing of an integer value, whereascout << "Enter a number"results in the printing of a string. The actions of the operators therefore depend on the types of supplied variables. - The extraction operator (
>>) performs a so called type safe assignment to a variable by `extracting' its value from a text stream. Normally, the extraction operator skips all whitespace characters preceding the values to be extracted. - Special symbolic constants are used for special situations. Normally a line is terminated by inserting
\nor\n. But when inserting theendlsymbol the line is terminated followed by the flushing of the stream's internal buffer. Thus,endlcan usually be avoided in favor of\nresulting in somewhat more efficient code.
The stream objects cin, cout and cerr are not part of the C++ grammar proper. The streams are part of the definitions in the header file iostream. This is comparable to functions like printf that are not part of the C grammar, but were originally written by people who considered such functions important and collected them in a run-time library.
A program may still use the old-style functions like printf and scanf rather than the new-style streams. The two styles can even be mixed. But streams offer several clear advantages and in many C++ programs have completely replaced the old-style C functions. Some advantages of using streams are:
- Using insertion and extraction operators is type-safe. The format strings which are used with
printfandscanfcan define wrong format specifiers for their arguments, for which the compiler sometimes can't warn. In contrast, argument checking withcin,coutandcerris performed by the compiler. Consequently it isn't possible to err by providing an int argument in places where, according to the format string, a string argument should appear. With streams there are no format strings. - The functions
printfandscanf(and other functions using format strings) in fact implement a mini-language which is interpreted at run-time. In contrast, with streams the C++ compiler knows exactly which in- or output action to perform given the arguments used. No mini-language here. - In addition the possibilities of the insertion and extraction operators may be extended allowing objects of classes that didn't exist when the streams were originally designed to be inserted into or extracted from streams. Mini languages as used with
printfcannot be extended. - The usage of the left-shift and right-shift operators in the context of the streams illustrates yet another capability of C++: operator overloading allowing us to redefine the actions an operator performs in certain contexts. Coming from C operator overloading requires some getting used to, but after a short little while these overloaded operators feel rather comfortable.
- Streams are independent of the media they operate upon. This (at this point somewhat abstract) notion means that the same code can be used without any modification at all to interface your code to any kind of device. The code using streams can be used when the device is a file on disk; an Internet connection; a digital camera; a DVD device; a satellite link; and much more: you name it. Streams allow your code to be decoupled (independent) of the devices your code is supposed to operate on, which eases maintenance and allows reuse of the same code in new situations.
The iostream library has a lot more to offer than just cin, cout and cerr. In chapter 6 iostreams are covered in greater detail. Even though printf and friends can still be used in C++ programs, streams have practically replaced the old-style C I/O functions like printf. If you think you still need to use printf and related functions, think again: in that case you've probably not yet completely grasped the possibilities of stream objects.
3.2: Functions as part of structs
Earlier we noted that functions can be part of structs (see section 2.5.13). Such functions are called member functions. This section briefly discusses how to define such functions.
The code fragment below shows a struct having data fields for a person's name and address. A function print is included in the struct's definition:
struct Person
{
char name[80];
char address[80];
void print();
};
When defining the member function print the structure's name (Person) and the scope resolution operator (::) are used:
void Person::print()
{
cout << "Name: " << name << "\n"
"Address: " << address << '\n';
}
The implementation of Person::print shows how the fields of the struct can be accessed without using the structure's type name. Here the function Person::print prints a variable name. Since Person::print is itself a part of struct person, the variable name implicitly refers to the same type.
This struct Person could be used as follows:
Person person;
strcpy(person.name, "Karel");
strcpy(person.address, "Marskramerstraat 33");
person.print();
The advantage of member functions is that the called function automatically accesses the data fields of the structure for which it was invoked. In the statement person.print() the object person is the substrate: the variables name and address that are used in the code of print refer to the data stored in the person object.
3.2.1: Data hiding: public, private and class
As mentioned before (see section 2.3), C++ contains specialized syntactic possibilities to implement data hiding. Data hiding is the capability of sections of a program to hide its data from other sections. This results in very clean data definitions. It also allows these sections to enforce the integrity of their data.
C++ has three keywords that are related to data hiding: private, protected and public. These keywords can be used in the definition of structs. The keyword public allows all subsequent fields of a structure to be accessed by all code; the keyword private only allows code that is part of the struct itself to access subsequent fields. The keyword protected is discussed in chapter 13, and is somewhat outside of the scope of the current discussion.
In a struct all fields are public, unless explicitly stated otherwise. Using this knowledge we can expand the struct Person:
struct Person
{
private:
char d_name[80];
char d_address[80];
public:
void setName(char const *n);
void setAddress(char const *a);
void print();
char const *name();
char const *address();
};
As the data fields d_name and d_address are in a private section they are only accessible to the member functions which are defined in the struct: these are the functions setName, setAddress etc.. As an illustration consider the following code:
Person fbb;
fbb.setName("Frank"); // OK, setName is public
strcpy(fbb.d_name, "Knarf"); // error, x.d_name is private
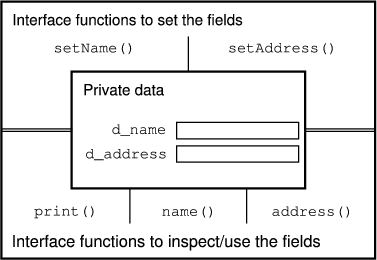
Data integrity is implemented as follows: the actual data of a struct Person are mentioned in the structure definition. The data are accessed by the outside world using special functions that are also part of the definition. These member functions control all traffic between the data fields and other parts of the program and are therefore also called interface functions. The thus implemented data hiding is illustrated in Figure 2.
The members setName and setAddress are declared with char const * parameters. This indicates that the functions will not alter the strings which are supplied as their arguments. Analogously, the members name and address return char const *: the compiler prevents callers of those members from modifying the information made accessible through the return values of those members.
Two examples of member functions of the struct Person are shown below:
void Person::setName(char const *n)
{
strncpy(d_name, n, 79);
d_name[79] = 0;
}
char const *Person::name()
{
return d_name;
}
The power of member functions and of the concept of data hiding results from the abilities of member functions to perform special tasks, e.g., checking the validity of the data. In the above example setName copies only up to 79 characters from its argument to the data member name, thereby avoiding a buffer overflow.
Another illustration of the concept of data hiding is the following. As an alternative to member functions that keep their data in memory a library could be developed featuring member functions storing data on file. To convert a program storing Person structures in memory to one that stores the data on disk no special modifications are required. After recompilation and linking the program to a new library it is converted from storage in memory to storage on disk. This example illustrates a broader concept than data hiding; it illustrates encapsulation. Data hiding is a kind of encapsulation. Encapsulation in general results in reduced coupling of different sections of a program. This in turn greatly enhances reusability and maintainability of the resulting software. By having the structure encapsulate the actual storage medium the program using the structure becomes independent of the actual storage medium that is used.
Though data hiding can be implemented using structs, more often (almost always) classes are used instead. A class is a kind of struct, except that a class uses private access by default, whereas structs use public access by default. The definition of a class Person is therefore identical to the one shown above, except that the keyword class has replaced struct while the initial private: clause can be omitted. Our typographic suggestion for class names (and other type names defined by the programmer) is to start with a capital character to be followed by the remainder of the type name using lower case letters (e.g., Person).
3.2.2: Structs in C vs. structs in C++
In this section we'll discuss an important difference between C and C++ structs and (member) functions. In C it is common to define several functions to process a struct, which then require a pointer to the struct as one of their arguments. An imaginary C header file showing this concept is:
/* definition of a struct PERSON This is C */
typedef struct
{
char name[80];
char address[80];
} PERSON;
/* some functions to manipulate PERSON structs */
/* initialize fields with a name and address */
void initialize(PERSON *p, char const *nm,
char const *adr);
/* print information */
void print(PERSON const *p);
/* etc.. */
In C++, the declarations of the involved functions are put inside the definition of the struct or class. The argument denoting which struct is involved is no longer needed.
class Person
{
char d_name[80];
char d_address[80];
public:
void initialize(char const *nm, char const *adr);
void print();
// etc..
};
In C++ the struct parameter is not used. A C function call such as:
PERSON x;
initialize(&x, "some name", "some address");
becomes in C++:
Person x;
x.initialize("some name", "some address");
3.3: Several additions to C's grammar
3.3.1: References
In addition to the common ways to define variables (plain variables or pointers) C++ introduces references defining synonyms for variables. A reference to a variable is like an alias; the variable and the reference can both be used in statements involving the variable:
int int_value;
int &ref = int_value;
In the above example a variable int_value is defined. Subsequently a reference ref is defined, which (due to its initialization) refers to the same memory location as int_value. In the definition of ref, the reference operator & indicates that ref is not itself an int but a reference to one. The two statements
++int_value;
++ref;
have the same effect: they increment int_value's value. Whether that location is called int_value or ref does not matter.
References serve an important function in C++ as a means to pass modifiable arguments to functions. E.g., in standard C, a function that increases the value of its argument by five and returning nothing needs a pointer parameter:
void increase(int *valp) // expects a pointer
{ // to an int
*valp += 5;
}
int main()
{
int x;
increase(&x); // pass x's address
}
This construction can also be used in C++ but the same effect is also achieved using a reference:
void increase(int &valr) // expects a reference
{ // to an int
valr += 5;
}
int main()
{
int x;
increase(x); // passed as reference
}
It is arguable whether code such as the above should be preferred over C's method, though. The statement increase (x) suggests that not x itself but a copy is passed. Yet the value of x changes because of the way increase() is defined. However, references can also be used to pass objects that are only inspected (without the need for a copy or a const *) or to pass objects whose modification is an accepted side-effect of their use. In those cases using references are strongly preferred over existing alternatives like copy by value or passing pointers.
Behind the scenes references are implemented using pointers. So, as far as the compiler is concerned references in C++ are just const pointers. With references, however, the programmer does not need to know or to bother about levels of indirection. An important distinction between plain pointers and references is of course that with references no indirection takes place. For example:
extern int *ip;
extern int &ir;
ip = 0; // reassigns ip, now a 0-pointer
ir = 0; // ir unchanged, the int variable it refers to
// is now 0.
In order to prevent confusion, we suggest to adhere to the following:
- In those situations where a function does not alter its parameters of a built-in or pointer type, value parameters can be used:
void some_func(int val)
{
cout << val << '\n';
}
int main()
{
int x;
some_func(x); // a copy is passed
}
- When a function explicitly must change the values of its arguments, a pointer parameter is preferred. These pointer parameters should preferably be the function's initial parameters. This is called return by argument.
void by_pointer(int *valp)
{
*valp += 5;
}
- When a function doesn't change the value of its class- or struct-type arguments, or if the modification of the argument is a trivial side-effect (e.g., the argument is a stream) references can be used. Const-references should be used if the function does not modify the argument:
void by_reference(string const &str)
{
cout << str; // no modification of str
}
int main ()
{
int x = 7;
by_pointer(&x); // a pointer is passed
// x might be changed
string str("hello");
by_reference(str); // str is not altered
}
- References play an important role in cases where the argument is not changed by the function but where it is undesirable to copy the argument to initialize the parameter. Such a situation occurs when a large object is passed as argument, or is returned by the function. In these cases the copying operation tends to become a significant factor, as the entire object must be copied. In these cases references are preferred.
If the argument isn't modified by the function, or if the caller shouldn't modify the returned information, the const keyword should be used. Consider the following example:
struct Person // some large structure
{
char name[80];
char address[90];
double salary;
};
Person person[50]; // database of persons
// printperson expects a
// reference to a structure
// but won't change it
void printperson (Person const &subject)
{
cout << "Name: " << subject.name << '\n' <<
"Address: " << subject.address << '\n';
}
// get a person by index value
Person const &personIdx(int index)
{
return person[index]; // a reference is returned,
} // not a copy of person[index]
int main()
{
Person boss;
printperson(boss); // no pointer is passed,
// so `boss' won't be
// altered by the function
printperson(personIdx(5));
// references, not copies
// are passed here
}
Furthermore, note that there is yet another reason for using references when passing objects as function arguments. When passing a reference to an object, the activation of a so called copy constructor is avoided. Copy constructors are covered in chapter 9.
References could result in extremely ugly code. A function may return a reference to a variable, as in the following example:
int &func()
{
static int value;
return value;
}
This allows the use of the following constructions:
func() = 20;
func() += func();
It is probably superfluous to note that such constructions should normally not be used. Nonetheless, there are situations where it is useful to return a reference. We have actually already seen an example of this phenomenon in our previous discussion of streams. In a statement like cout << "Hello" << '\n'; the insertion operator returns a reference to cout. So, in this statement first the Hello is inserted into cout, producing a reference to cout. Through this reference the \n is then inserted in the cout object, again producing a reference to cout, which is then ignored.
Several differences between pointers and references are pointed out in the next list below:
- A reference cannot exist by itself, i.e., without something to refer to. A declaration of a reference like
int &ref; is not allowed; what wouldrefrefer to? - References can be declared as external. These references were initialized elsewhere.
- References may exist as parameters of functions: they are initialized when the function is called.
- References may be used in the return types of functions. In those cases the function determines what the return value refers to.
- References may be used as data members of classes. We return to this usage later.
- Pointers are variables by themselves. They point at something concrete or just ``at nothing''.
- References are aliases for other variables and cannot be re-aliased to another variable. Once a reference is defined, it refers to its particular variable.
- Pointers (except for const pointers) can be reassigned to point to different variables.
- When an address-of operator & is used with a reference, the expression yields the address of the variable to which the reference applies. In contrast, ordinary pointers are variables themselves, so the address of a pointer variable has nothing to do with the address of the variable pointed to.
3.3.2: Rvalue References
In C++, temporary (rvalue) values are indistinguishable from const & types. C++ introduces a new reference type called an rvalue reference, which is defined as typename &&.
The name rvalue reference is derived from assignment statements, where the variable to the left of the assignment operator is called an lvalue and the expression to the right of the assignment operator is called an rvalue. Rvalues are often temporary, anonymous values, like values returned by functions.
In this parlance the C++ reference should be considered an lvalue reference (using the notation typename &). They can be contrasted to rvalue references (using the notation typename &&).
The key to understanding rvalue references is the concept of an anonymous variable. An anonymous variable has no name and this is the distinguishing feature for the compiler to associate it automatically with an rvalue reference if it has a choice. Before introducing some interesting constructions let's first have a look at some standard situations where lvalue references are used. The following function returns a temporary (anonymous) value:
int intVal()
{
return 5;
}
Although intVal's return value can be assigned to an int variable it requires copying, which might become prohibitive when a function does not return an int but instead some large object. A reference or pointer cannot be used either to collect the anonymous return value as the return value won't survive beyond that. So the following is illegal (as noted by the compiler):
int &ir = intVal(); // fails: refers to a temporary
int const &ic = intVal(); // OK: immutable temporary
int *ip = &intVal(); // fails: no lvalue available
Apparently it is not possible to modify the temporary returned by intVal. But now consider these functions:
void receive(int &value) // note: lvalue reference
{
cout << "int value parameter\n";
}
void receive(int &&value) // note: rvalue reference
{
cout << "int R-value parameter\n";
}
and let's call this function from main:
int main()
{
receive(18);
int value = 5;
receive(value);
receive(intVal());
}
This program produces the following output:
int R-value parameter
int value parameter
int R-value parameter
The program's output shows the compiler selecting receive(int &&value) in all cases where it receives an anonymous int as its argument. Note that this includes receive(18): a value 18 has no name and thus receive(int &&value) is called. Internally, it actually uses a temporary variable to store the 18, as is shown by the following example which modifies receive:
void receive(int &&value)
{
++value;
cout << "int R-value parameter, now: " << value << '\n';
// displays 19 and 6, respectively.
}
Contrasting receive(int &value) with receive(int &&value) has nothing to do with int &value not being a const reference. If receive(int const &value) is used the same results are obtained. Bottom line: the compiler selects the overloaded function using the rvalue reference if the function is passed an anonymous value.
The compiler runs into problems if void receive(int &value) is replaced by void receive(int value), though. When confronted with the choice between a value parameter and a reference parameter (either lvalue or rvalue) it cannot make a decision and reports an ambiguity. In practical contexts this is not a problem. Rvalue references were added to the language in order to be able to distinguish the two forms of references: named values (for which lvalue references are used) and anonymous values (for which rvalue references are used).
It is this distinction that allows the implementation of move semantics and perfect forwarding. At this point the concept of move semantics cannot yet fully be discussed (but see section 9.7 for a more thorough discussion) but it is very well possible to illustrate the underlying ideas.
Consider the situation where a function returns a struct Data containing a pointer to a dynamically allocated NTBS. We agree that Data objects are only used after initialization, for which two init functions are available. As an aside: when Data objects are no longer required the memory pointed at by text must again be returned to the operating system; assume that that task is properly performed.
struct Data
{
char *text;
void init(char const *txt); // initialize text from txt
void init(Data const &other)
{
text = strdup(other.text);
}
};
There's also this interesting function:
Data dataFactory(char const *text);
Its implementation is irrelevant, but it returns a (temporary) Data object initialized with text. Such temporary objects cease to exist once the statement in which they are created end.
Now we'll use Data:
int main()
{
Data d1;
d1.init(dataFactory("object"));
}
Here the init function duplicates the NTBS stored in the temporary object. Immediately thereafter the temporary object ceases to exist. If you think about it, then you realize that that's a bit over the top:
- the
dataFactoryfunction usesinitto initialize thetextvariable of its temporary Data object. For that it usesstrdup; - the
d1.initfunction then also usesstrdupto initialized1.text; - the statement ends, and the temporary object ceases to exist.
That's two strdup calls, but the temporary Data object thereafter is never used again.
To handle cases like these rvalue reference were introduced. We add the following function to the struct Data:
void init(Data &&tmp)
{
text = tmp.text; // (1)
tmp.text = 0; // (2)
}
Now, when the compiler translates d1.init(dataFactory("object")) it notices that dataFactory returns a (temporary) object, and because of that it uses the init(Data &&tmp) function. As we know that the tmp object ceases to exist after executing the statement in which it is used, the d1 object (at (1)) grabs the temporary object's text value, and then (at (2)) assigns 0 to other.text so that the temporary object's free(text) action does no harm.
Thus, struct Data suddenly has become move-aware and implements move semantics, removing the (extra copy) drawback of the previous approach, and instead of making an extra copy of the temporary object's NTBS the pointer value is simply transferred to its new owner.
3.3.3: Lvalues, rvalues and more
Although this section contains forward references to chapters 5, 7, and 16, its topic best fits the current chapter. This section can be skipped without loss of continuity, and you might consider returning to it once you're familiar with the content of these future chapters.
Historically, the C programming language distinguished between lvalues and rvalues. The terminology was based on assignment expressions, where the expression to the left of the assignment operator receives a value (e.g., it referred to a location in memory where a value could be written into, like a variable), while the expression to the right of the assignment operator only had to represent a value (it could be a temporary variable, a constant value or the value stored in a variable):
lvalue = rvalue;
C++ adds to this basic distinction several new ways of referring to expressions:
- lvalue: an lvalue in C++ has the same meaning as in C. It refers to a location where a value can be stored, like a variable, a reference to a variable, or a dereferenced pointer.
- xvalue: an xvalue indicates an expiring value. An expiring value refers to an object (cf. chapter 7) just before its lifetime ends. Such objects normally have to make sure that resources they own (like dynamically allocated memory) also cease to exist, but such resources may, just before the object's lifetime ends, be moved to another location, thus preventing their destruction.
- glvalue: a glvalue is a generalized lvalue. A generalized lvalue refers to anything that may receive a value. It is either an lvalue or an xvalue.
- prvalue: a prvalue is a pure rvalue: a literal value (like 1.2e3) or an immutable object (e.g., the value returned from a function returning a constant
std::string(cf. chapter 5)).
An expression's value is an xvalue if it is:
-
the value returned by a function returning an rvalue reference to an object;
-
an object that is cast to an rvalue reference;
-
an expression accessing a non-static class data member whose object is
- an xvalue, or
- a . (pointer-to-member) expression* (cf. chapter 16) in which the left-hand side operand is an xvalue and the right-hand side operand is a pointer to a data member.
The effect of this rule is that named rvalue references are treated as lvalues and anonymous rvalue references to objects are treated as xvalues.
Rvalue references to functions are treated as lvalues whether anonymous or not.
Here is a small example. Consider this simple struct:
struct Demo
{
int d_value;
};
In addition we have these function declarations and definitions:
Demo &&operator+(Demo const &lhs, Demo const &rhs);
Demo &&factory();
Demo demo;
Demo &&rref = static_cast<Demo &&>(demo);
Expressions like
factory();
factory().d_value;
static_cast<Demo &&>(demo);
demo + demo
are xvalues. However, the expression
rref;
is an lvalue.
In many situations it's not particularly important to know what kind of lvalue or what kind of rvalue is actually used. In the C++ Annotations the term lhs (left hand side) is frequently used to indicate an operand that's written to the left of a binary operator, while the term rhs (right hand side) is frequently used to indicate an operand that's written to the right of a binary operator. Lhs and rhs operands could actually be gvalues (e.g., when representing ordinary variables), but they could also be prvalues (e.g., numeric values added together using the addition operator). Whether or not lhs and rhs operands are gvalues or lvalues can always be determined from the context in which they are used.
3.3.4: Strongly typed enumerations
Enumeration values in C++ are in fact int values, thereby bypassing type safety. E.g., values of different enumeration types may be compared for (in)equality, albeit through a (static) type cast.
Another problem with the current enum type is that their values are not restricted to the enum type name itself, but to the scope where the enumeration is defined. As a consequence, two enumerations having the same scope cannot have identical names.
Such problems are solved by defining enum classes. An enum class can be defined as in the following example:
enum class SafeEnum
{
NOT_OK, // 0, by implication
OK = 10,
MAYBE_OK // 11, by implication
};
Enum classes use int values by default, but the used value type can easily be changed using the : type notation, as in:
enum class CharEnum: unsigned char
{
NOT_OK,
OK
};
To use a value defined in an enum class its enumeration name must be provided as well. E.g., OK is not defined, CharEnum::OK is.
Using the data type specification (noting that it defaults to int) it is possible to use enum class forward declarations. E.g.,
enum Enum1; // Illegal: no size available
enum Enum2: unsigned int; // Legal: explicitly declared type
enum class Enum3; // Legal: default int type is used
enum class Enum4: char; // Legal: explicitly declared type
A sequence of symbols of a strongly typed enumeration can also be indicated in a switch using the ellipsis syntax, as shown in the next example:
SafeEnum enumValue();
switch (enumValue())
{
case SafeEnum::NOT_OK ... SafeEnum::OK:
cout << "Status is known\n";
break;
default:
cout << "Status unknown\n";
break;
}
3.3.5: Initializer lists
The C language defines the initializer list as a list of values enclosed by curly braces, possibly themselves containing initializer lists. In C these initializer lists are commonly used to initialize arrays and structs.
C++ extends this concept by introducing the type initializer_list<Type> where Type is replaced by the type name of the values used in the initializer list. Initializer lists in C++ are, like their counterparts in C, recursive, so they can also be used with multi-dimensional arrays, structs and classes.
Before using the initializer_list the <initializer_list> header file must be included.
Like in C, initializer lists consist of a list of values surrounded by curly braces. But unlike C, functions can define initializer list parameters. E.g.,
void values(std::initializer_list<int> iniValues)
{
}
A function like values could be called as follows:
values({2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13});
The initializer list appears as an argument which is a list of values surrounded by curly braces. Due to the recursive nature of initializer lists a two-dimensional series of values can also be passes, as shown in the next example:
void values2(std::initializer_list<std::initializer_list<int>> iniValues)
{}
values2({{1, 2}, {2, 3}, {3, 5}, {4, 7}, {5, 11}, {6, 13}});
Initializer lists are constant expressions and cannot be modified. However, their size and values may be retrieved using their size, begin, and end members as follows:
void values(initializer_list<int> iniValues)
{
cout << "Initializer list having " << iniValues.size() << "values\n";
for
(
initializer_list<int>::const_iterator begin = iniValues.begin();
begin != iniValues.end();
++begin
)
cout << "Value: " << *begin << '\n';
}
Initializer lists can also be used to initialize objects of classes (cf. section 7.5, which also summarizes the facilities of initializer lists).
Implicit conversions, also called narrowing conversions are not allowed when specifying values of initializer lists. Narrowing conversions are encountered when values are used of a type whose range is larger than the type specified when defining the initializer list. For example
- specifying float or double values to define initializer lists of int values;
- specifying integral values exceeding the range of float to define initializer lists of float values;
- specifying values of integral types of a wider range than the integral type that is specified for the initializer list, except if the specified values lie within the range of the initializer list's integral type
Some examples:
initializer_list<int> ii{ 1.2 }; // 1.2 isn't an int value
initializer_list<unsigned> iu{ ~0ULL }; // unsigned long long doesn't fit
3.3.5.1: Designated initialization
C++, like C, also supports designated initialization. However, as C++ requires that destruction of data members occurs in the opposite order as their construction it is required that, when using designated initialization, members are initialized in the order in which they are declared in their class or struct. E.g.,
struct Data
{
int d_first;
double d_second;
std::string d_third;
};
Data data{ .d_first = 1, .d_third = "hello" };
In this example, d_first and d_third are explicitly initialized, while d_second is implicitly initialized to its default value (so: 0.0).
In C++ it is not allowed to reorder the initialization of members in a desginated initialization list. So, Data data{ .d_third = "hello", .d_first = 1 } is an error, but Data data{ .d_third = "hello" } is OK, as there is no ordering conflict in the latter example (this also initializes d_first and d_second to 0).
Likewise, a union can be initialized using designated initialization, as illustrated by the next example:
union Data
{
int d_first;
double d_second;
std::string *d_third;
};
// initialize the union's d_third field:
Data data{ .d_third = new string{ "hello" } };
3.3.6: Initializers for bit-fields
Bit-fields are used to specify series of bits in an integral value type. For example, in networking software processing IP4 packets, the first uint32_t value of IP4 packets contain:
- the version (4 bits);
- the header length (4 bits);
- the type of service (8 bits);
- the total length (16 bits)
Rather than using complex bit and bit-shift operations, these fields inside integral values can be specified using bit-fields. E.g.,
struct FirstIP4word
{
uint32_t version: 4;
uint32_t header: 4;
uint32_t tos: 8;
uint32_t length: 16;
};
To total size of a FirstIP4word object is 32 bits, or four bytes. To show the version of a FirstIP4word first object, simply do:
cout << first.version << '\n';
and to set its header length to 10 simply do
first.header = 10;
Bit fields are already available in C. The C++23 standard allows them to be initialized by default by using initialization expressions in their definitions. E.g.,
struct FirstIP4word
{
uint32_t version: 4 = 1; // version now 1, by default
uint32_t header: 4 = 10; // TCP header length now 10, by default
uint32_t tos: 8;
uint32_t length: 16;
};
The initialization expressions are evaluated when the object using the bit-fields is defined. Also, when a variable is used to initialize a bit-field the variable must at least have been declared when the struct containing bit-fields is defined. E.g.,
extern int value;
struct FirstIP4word
{
...
uint32_t length: 16 = value; // OK: value has been declared
};
3.3.7: Type inference using auto
The keyword auto can be used to simplify type definitions of variables and return types of functions if the compiler is able to determine the proper types of such variables or functions.
Using auto as a storage class specifier is no longer supported by C++: a variable definition like auto int var results in a compilation error.
The keyword auto is used in situations where it is very hard to determine the variable's type. These situations are encountered, e.g., in the context of templates (cf. chapters 18 until 23). It is also used in situations where a known type is a very long one but also automatically available to the compiler. In such cases the programmer uses auto to avoid having to type long type definitions.
At this point in the Annotations only simple examples can be given. Refer to section 21.1.2 for additional information about auto (and the related decltype function).
When defining and initializing a variable int variable = 5 the type of the initializing expression is well known: it's an int, and unless the programmer's intentions are different this could be used to define variable's type (a somewhat contrived example as in this case it reduces rather than improves the clarity of the code):
auto variable = 5;
However, it is attractive to use auto. In chapter 5 the iterator concept is introduced (see also chapters 12 and 18). Iterators frequently have long type definitions, like
std::vector<std::string>::const_reverse_iterator
Functions may return objects having such types. Since the compiler knows about these types we may exploit this knowledge by using auto. Assume that a function begin() is declared like this:
std::vector<std::string>::const_reverse_iterator begin();
Rather than writing a long variable definition (at // 1, below) a much shorter definition (at // 2) can be used:
std::vector<std::string>::const_reverse_iterator iter = begin(); // 1
auto iter = begin(); // 2
It's also easy to define and initialize additional variables of such types. When initializing such variables iter can be used to initialize those variables, and auto can be used, so the compiler deduces their types:
auto start = iter;
When defining variables using auto the variable's type is deduced from the variable's initializing expression. Plain types and pointer types are used as-is, but when the initializing expression is a reference type, then the reference's basic type (without the reference, omitting const or volatile specifications) is used.
If a reference type is required then auto & or auto && can be used. Likewise, const and/or pointer specifications can be used in combination with the auto keyword itself. Here are some examples:
int value;
auto another = value; // 'int another' is defined
string const &text();
auto str = text(); // text's plain type is string, so
// string str, NOT string const str
// is defined
str += "..."; // so, this is OK
int *ip = &value;
auto ip2 = ip; // int *ip2 is defined.
int *const &ptr = ip;
auto ip3 = ptr; // int *ip3 is defined, omitting const &
auto const &ip4 = ptr; // int *const &ip4 is defined.
In the next to last auto specification, the tokens (reading right to left) from the reference to the basic type are omitted: here const & was appended to ptr's basic type (int *). Hence, int *ip2 is defined.
In the last auto specification auto also produces int *, but in the type definition const & is added to the type produced by auto, so int *const &ip4 is defined.
The auto keyword can also be used to postpone the definition of a function's return type. The declaration of a function intArrPtr returning a pointer to arrays of 10 ints looks like this:
int (*intArrPtr())[10];
Such a declaration is fairly complex. E.g., among other complexities it requires protection of the pointer using parentheses in combination with the function's parameter list. In situations like these the specification of the return type can be postponed using the auto return type, followed by the specification of the function's return type after any other specification the function might receive (e.g., as a const member (cf. section 7.7) or following its noexcept specification (cf. section 23.8)).
Using auto to declare the above function, the declaration becomes:
auto intArrPtr() -> int (*)[10];
A return type specification using auto is called a late-specified return type.
Since the C++14 standard late return type specifications are no longer required for functions returning auto. Such functions can now simply be declared like this:
auto autoReturnFunction();
In this case some restrictions apply, both to the function definitions and the function declarations:
- If multiple return statements are used in function definitions they all must return values of identical types;
- Functions merely returning
autocannot be used before the compiler has seen their definitions. So they cannot be used after mere declarations; - When functions returning
autoare implemented as recursive function then at least one return statement must have been seen before the recursive call. E.g.,
auto fibonacci(size_t n)
{
if (n <= 1)
return n;
return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2);
}
3.3.7.1: Structured binding declarations
Usually functions return single-valued results: doubles, ints, strings, etc. When functions need to return multiple values a return by argument construction is often used, where addresses of variables that live outside of the called function are passed to functions, allowing the functions to assign new values to those variables.
When multiple values should be returned from a function a struct can be used, but pairs (cf. section 12.2) or tuples (cf. section 22.6) can also be used. Here's a simple example, where a function fun returns a struct having two data fields:
struct Return
{
int first;
double second;
};
Return fun()
{
return Return{ 1, 12.5 };
}
(Briefly forward referencing to sections 12.2 and 22.6: the struct definition can completely be omitted if fun returns a pair or tuple. In those cases the following code remains valid.)
A function calling fun traditionally defines a variable of the same type as fun's return type, and then uses that variable's fields to access first and second. If you don't like the typing, auto can also be used:
int main()
{
auto r1 = fun();
cout << r1.first;
}
Instead of referring to the elements of the returned struct, pair or tuple structured binding declarations can also be used. Here, auto is followed by a (square brackets surrounded) comma-separated list of variables, where each variable is defined, and receives the value of the corresponding field or element of the called function's return value. So, the above main function can also be written like this:
int main()
{
auto [one, two] = fun();
cout << one; // one and two: now defined
}
Merely specifying auto results in fun's return value being copied, and the structured bindings variables will refer to the copied value. But structured binding declarations can also be used in combination with (lvalue/rvalue) return values. The following ensures that rone and rtwo refer to the elements of fun's anonymous return value:
int main()
{
auto &&[rone, rtwo] = fun();
}
If the called function returns a value that survives the function call itself, then structured binding declarations can use lvalue references. E.g.,
Return &fun2()
{
static Return ret{ 4, 5 };
return ret;
}
int main()
{
auto &[lone, ltwo] = fun2(); // OK: referring to ret's fields
}
To use structured binding declarations it is not required to use function calls. The object providing the data can also anonymously be defined:
int main()
{
auto const &[lone, ltwo] = Return{ 4, 5 };
// or:
auto &&[lone, ltwo] = Return{ 4, 5 };
}
The object doesn't even have to make its data members publicly available. In section TUPLES using structured bindings not necessarily referring to data members is covered.
Another application is found in situations where nested statements of for or selection statements benefit from using locally defined variables of various types. Such variables can easily be defined using structured binding declarations that are initialized from anonymous structs, pairs or tuples. Here is an example illustrating this:
// define a struct:
struct Three
{
size_t year;
double firstAmount;
double interest;
};
// define an array of Three objects, and process each in turn:
Three array[10];
fill(array); // not implemented here
for (auto &[year, amount, interest]: array)
cout << "Year " << year << ": amount = " << amount << '\n';
When using structured bindings the structured binding declaration must specify all elements that are available. So if a struct has four data members the structured binding declaration must define four elements. To avoid warnings of unused variables at lease one of the variables of the structured binding declaration must be used.
3.3.8: Defining types and using declarations
In C++ typedef is commonly used to define shorthand notations for complex types. Assume we want to define a shorthand for a pointer to a function expecting a double and an int, and returning an unsigned long long int. Such a function could be:
unsigned long long int compute(double, int);
A pointer to such a function has the following form:
unsigned long long int (*pf)(double, int);
If this kind of pointer is frequently used, consider defining it using typedef: simply put typedef in front of it and the pointer's name is turned into the name of a type. It could be capitalized to let it stand out more clearly as the name of a type:
typedef unsigned long long int (*PF)(double, int);
After having defined this type, it can be used to declare or define such pointers:
PF pf = compute; // initialize the pointer to a function like
// 'compute'
void fun(PF pf); // fun expects a pointer to a function like
// 'compute'
However, including the pointer in the typedef might not be a very good idea, as it masks the fact that pf is a pointer. After all, PF pf looks more like int x than int *x. To document that pf is in fact a pointer, slightly change the typedef:
typedef unsigned long long int FUN(double, int);
FUN *pf = compute; // now pf clearly is a pointer.
The scope of typedefs is restricted to compilation units. Therefore, typedefs are usually embedded in header files which are then included by multiple source files in which the typedefs should be used.
In addition to typedef C++ offers the using keyword to associate a type and an identifier. In practice typedef and using can be used interchangeably. The using keyword arguably result in more readable type definitions. Consider the following three (equivalent) definitions:
-
The traditional, C style definition of a type, embedding the type name in the definition (turning a variable name into a type name):
typedef unsigned long long int FUN(double, int); -
Apply using to improve the visibility (for humans) of the type name, by moving the type name to the front of the definition:
using FUN = unsigned long long int (double, int); -
An alternative construction, using a late-specified return type (cf. section [3.3.7]({{< relref "/docs/A First Impression/#337-type-inference-using-auto" >}})):
using FUN = auto (double, int) -> unsigned long long int;
3.3.9: Range-based for-loops
The C++ for-statement is identical to C's for-statement:
for (init; cond; inc)
statement
Often the initialization, condition, and increment parts are fairly obvious, as in situations where all elements of an array or vector must be processed. Many languages offer the foreach statement for that and C++ offers the std::for_each generic algorithm (cf. section 19.1.18).
In addition to the traditional syntax C++ adds new syntax for the for-statement: the range-based for-loop. This new syntax can be used to process all element of a range in turn. Three types of ranges are distinguished:
- Plain arrays (e.g.,
int array[10]); - Initializer lists;
- Standard containers (or comparable) (cf. chapter 12);
- Any other type offering
begin()andend()functions returning so-called iterators (cf. section 18.2).
The following additional for-statement syntax is available:
// assume int array[30]
for (auto &element: array)
statement
The part to the left of the colon is called the for range declaration. The declared variable (element) is a formal name; use any identifier you like. The variable is only available within the nested statement, and it refers to (or is a copy of) each of the elements of the range, from the first element up to the last.
There's no formal requirement to use auto, but using auto is extremely useful in many situations. Not only in situations where the range refers to elements of some complex type, but also in situations where you know what you can do with the elements in the range, but don't care about their exact type names. In the above example int could also have been used.
The reference symbol (&) is important in the following cases:
- if you want to modify the elements in the nested statements
- if the elements themselves are structs (or classes, cf. chapter 7)
When the reference symbol is omitted the variable will be a copy of each of the subsequent elements of the range. Fine, probably, if you merely need to look at the variables when they are of primitive types, but needlessly inefficient if you have an array of BigStruct elements:
struct BigStruct
{
double array[100];
int last;
};
Inefficient, because you don't need to make copies of the array's elements. Instead, use references to elements:
BigStruct data[100]; // assume properly initialized elsewhere
int countUsed()
{
int sum = 0;
// const &: the elements aren't modified
for (auto const &element: data)
sum += element.last;
return sum;
}
Range-based for-loops can also benefit from structured bindings. If struct Element holds a int key and a double value, and all the values of positive keys should be added then the following code snippet accomplishes that:
Element elems[100]; // somehow initialized
double sum = 0;
for (auto const &[key, value]: elems)
{
if (key > 0)
sum += value;
}
The C++23 standard also supports an optional initialization section (like the ones already available for if and switch statements) for range-based for-loops. Assume the elements of an array must be inserted into cout, but before each element we want to display the element's index. The index variable is not used outside the for-statement, and the extension offered in the C++23 standard allows us to localize the index variable. Here is an example:
// localize idx: only visible in the for-stmnt
for (size_t idx = 0; auto const &element: data)
cout << idx++ << ": " << element << '\n';
3.3.10: Raw String Literals
Standard series of ASCII characters (a.k.a. C strings) are delimited by double quotes, supporting escape sequences like \n, \\ and \", and ending in 0-bytes. Such series of ASCII-characters are commonly known as null-terminated byte strings (singular: NTBS, plural: NTBSs). C's NTBS is the foundation upon which an enormous amount of code has been built
In some cases it is attractive to be able to avoid having to use escape sequences (e.g., in the context of XML). C++ allows this using raw string literals.
Raw string literals start with an R, followed by a double quote, optionally followed by a label (which is an arbitrary sequence of non-blank characters, followed by (). The raw string ends at the closing parenthesis ), followed by the label (if specified when starting the raw string literal), which is in turn followed by a double quote. Here are some examples:
R"(A Raw \ "String")"
R"delimiter(Another \ Raw "(String))delimiter"
In the first case, everything between "( and )" is part of the string. Escape sequences aren't supported so the text \ " within the first raw string literal defines three characters: a backslash, a blank character and a double quote. The second example shows a raw string defined between the markers "delimiter( and )delimiter".
Raw string literals come in very handy when long, complex ascii-character sequences (e.g., usage-info or long html-sequences) are used. In the end they are just that: long NTBSs. Those long raw string literals should be separated from the code that uses them, thus maintaining the readability of the using code.
As an illustration: the bisonc++ parser generator supports an option --prompt. When specified, the code generated by bisonc++ inserts prompting code when debugging is requested. Directly inserting the raw string literal into the function processing the prompting code results in code that is very hard to read:
void prompt(ostream &out)
{
if (d_genDebug)
out << (d_options.prompt() ? R"(
if (d_debug__)
{
s_out__ << "\n================\n"
"? " << dflush__;
std::string s;
getline(std::cin, s);
}
)" : R"(
if (d_debug__)
s_out__ << '\n';
)"
) << '\n';
}
Readability is greatly enhanced by defining the raw string literals as named NTBSs, defined in the source file's anonymous namespace (cf. chapter [4]({{< relref "/docs/Name Spaces" >}})):
namespace {
char const noPrompt[] =
R"(
if (d_debug__)
s_out__ << '\n';
)";
char const doPrompt[] =
R"(
if (d_debug__)
{
s_out__ << "\n================\n"
"? " << dflush__;
std::string s;
getline(std::cin, s);
}
)";
} // anonymous namespace
void prompt(ostream &out)
{
if (d_genDebug)
out << (d_options.prompt() ? doPrompt : noPrompt) << '\n';
}
3.3.11: Binary constants
In addition to hexadecimal integral constants (starting with 0x), octal integral constants (starting with 0), and decimal integral constants (starting with one of the digits 1..9), binary integral constants can be defined using the prefixes 0b or 0B. E.g., to represent the (decimal) value 5 the notation 0b101 can also be used.
The binary constants come in handy in the context of, e.g., bit-flags, as it immediately shows which bit-fields are set, while other notations are less informative.
3.3.12: Selection statements with initializers
The standard for repetition statements start with an optional initialization clause. The initialization clause allows us to localize variables to the scope of the for statements. Initialization clauses van also be used in selection statements.
Consider the situation where an action should be performed if the next line read from the standard input stream equals go!. Traditionally, when used inside a function, intending to localize the string to contain the content of the next line as much as possible, constructions like the following had to be used:
void function()
{
// ... any set of statements
{
string line; // localize line
if (getline(cin, line))
action();
}
// ... any set of statements
}
Since init ; clauses can also be used for selection statements (if and switch statements) (note that with selection statements the semicolon is part of the initialization clause, which is different from the optional init (no semicolon) clause in for statements), we can rephrase the above example as follows:
void function()
{
// ... any set of statements
if (string line; getline(cin, line))
action();
// ... any set of statements
}
Note that a variable may still also be defined in the actual condition clauses. This is true for both the extended if and switch statement. However, before using the condition clauses an initialization clause may be used to define additional variables (plural, as it may contain a comma-separated list of variables, similar to the syntax that's available for for-statements).
3.3.13: Attributes
Attributes are compiler directives that are inserted into source files to inform the compiler of some peculiarity of the code (variable or function) that follows the specified attribute. Attributes are used to inform the compiler about situations that are intentional, and thus prevent the compiler from issuing warnings.
The following attributes are recognized:
-
This attribute is currently not yet covered by the C++ Annotations. At this point in the C++ Annotations it can safely be ignored.
-
This attribute (and its alternative form
[[deprecated("reason")]]) is available since the C++14 standard. It indicates that the use of the name or entity declared with this attribute is allowed, but discouraged for some reason. This attribute can be used for classes, typedef-names, variables, non-static data members, functions, enumerations, and template specializations. An existing non-deprecated entity may be redeclared deprecated, but once an entity has been declared deprecated it cannot be redeclared asundeprecated'. When encountering thedeprecated` attribute the compiler generates a warning, e.g.,demo.cc:12:24: warning: 'void deprecatedFunction()' is deprecated [-Wdeprecated-declarations] deprecatedFunction(); demo.cc:5:21: note: declared here [[deprecated]] void deprecatedFunction()When using the alternative form (e.g.,
[[deprecated("do not use")]] void fun())the compiler generates a warning showing the text between the double quotes, e.g.,demo.cc:12:24: warning: 'void deprecatedFunction()' is deprecated: do not use [-Wdeprecated-declarations] deprecatedFunction(); demo.cc:5:38: note: declared here [[deprecated("do not use")]] void deprecatedFunction() -
When statements nested under case entries in switch statements continue into subsequent case or default entries the compiler issues a
falling throughwarning. If falling through is intentional the attribute[[fallthrough]], which then must be followed by a semicolon, should be used. Here is an annotated example:void function(int selector) { switch (selector) { case 1: case 2: // no falling through, but merged entry points cout << "cases 1 and 2\n"; [[fallthrough]]; // no warning: intentionally falling through case 3: cout << "case 3\n"; case 4: // a warning is issued: falling through not // announced. cout << "case 4\n"; [[fallthrough]]; // error: there's nothing beyond } } -
This attribute can be applied to a class, typedef-name, variable, parameter, non-static data member, a function, an enumeration or an enumerator. When it is applied to an entity no warning is generated when the entity is not used. Example:
void fun([[maybe_unused]] size_t argument) { // argument isn't used, but no warning // telling you so is issued } -
The attribute
[[nodiscard]]may be specified when declaring a function, class or enumeration. If a function is declared[[nodiscard]]or if a function returns an entity previously declared using[[nodiscard]]then the return value of such a function may only be ignored when explicitly cast to void. Otherwise, when the return value is not used a warning is issued. Example:int [[nodiscard]] importantInt(); struct [[nodiscard]] ImportantStruct { ... }; ImportantStruct factory(); int main() { importantInt(); // warning issued factory(); // warning issued } -
[[noreturn]]indicates that the function does not return.[noreturn]]'s behavior is undefined if the function declared with this attribute actually returns. The following standard functions have this attribute:std::_Exit,std::abort,std::exit,std::quick_exit,std::unexpected,std::terminate,std::rethrow_exception,std::throw_with_nested,std::nested_exception::rethrow_nested, Here is an example of a function declaration and definition using the[[noreturn]]attribute:[[noreturn]] void doesntReturn(); [[noreturn]] void doesntReturn() { exit(0); }
3.3.14: Three-way comparison (<=>)
The C++23 standard added the three-way comparison operator <=>, also known as the spaceship operator, to C++. In C++ operators can be defined for class-types, among which equality and comparison operators (the familiar set of ==, !=, <, <=, > and >= operators). To provide classes with all comparison operators merely the the equality and the spaceship operator need to be defined.
Its priority is less than the priorities of the bit-shift operators << and >> and larger than the priorities of the ordering operators <, <=, >, and >=.
Section 11.7.2 covers the construction of the three-way comparison operator.
3.4: New language-defined data types
In C the following built-in data types are available: void, char, short, int, long, float and double. C++ extends these built-in types with several additional built-in types: the types bool, wchar_t, long long and long double (Cf. ANSI/ISO draft (1995), par. 27.6.2.4.1 for examples of these very long types). The type long long is merely a double-long long datatype. The type long double is merely a double-long double datatype. These built-in types as well as pointer variables are called primitive types in the C++ Annotations.
There is a subtle issue to be aware of when converting applications developed for 32-bit architectures to 64-bit architectures. When converting 32-bit programs to 64-bit programs, only long types and pointer types change in size from 32 bits to 64 bits; integers of type int remain at their size of 32 bits. This may cause data truncation when assigning pointer or long types to int types. Also, problems with sign extension can occur when assigning expressions using types shorter than the size of an int to an unsigned long or to a pointer. More information about this issue can be found here.
Except for these built-in types the class-type string is available for handling character strings. The datatypes bool, and wchar_t are covered in the following sections, the datatype string is covered in chapter 5. Note that recent versions of C may also have adopted some of these newer data types (notably bool and wchar_t). Traditionally, however, C doesn't support them, hence they are mentioned here.
Now that these new types are introduced, let's refresh your memory about letters that can be used in literal constants of various types. They are:
- b or B: in addition to its use as a hexadecimal value, it can also be used to define a binary constant. E.g.,
0b101equals the decimal value 5. The0bprefix can be used to specify binary constants starting with the C++14 standard. - E or e: the exponentiation character in floating point literal values. For example:
1.23E+3. Here,Eshould be pronounced (and interpreted) as: times 10 to the power. Therefore,1.23E+3represents the value 1230. - F can be used as postfix to a non-integral numeric constant to indicate a value of type float, rather than double, which is the default. For example:
12.F(the dot transforms 12 into a floating point value);1.23E+3F(see the previous example.1.23E+3is a double value, whereas1.23E+3Fis a float value). - L can be used as prefix to indicate a character string whose elements are wchar_t-type characters. For example:
L"hello world". - L can be used as postfix to an integral value to indicate a value of type
long, rather thanint, which is the default. Note that there is no letter indicating a short type. For that astatic_cast<short>()must be used. - p, to specify the power in hexadecimal floating point numbers. E.g.
0x10p4. The exponent itself is read as a decimal constant and can therefore not start with0x. The exponent part is interpreted as a power of 2. So0x10p2is (decimal) equal to 64: 16 * 2^2. - U can be used as postfix to an integral value to indicate an
unsignedvalue, rather than anint. It may also be combined with the postfixLto produce anunsigned long intvalue.
And, of course: the x and a until f characters can be used to specify hexadecimal constants (optionally using capital letters).
3.4.1: The data type bool
The type bool represents boolean (logical) values, for which the (now reserved) constants true and false may be used. Except for these reserved values, integral values may also be assigned to variables of type bool, which are then implicitly converted to true and false according to the following conversion rules (assume intValue is an int-variable, and boolValue is a bool-variable):
// from int to bool:
boolValue = intValue ? true : false;
// from bool to int:
intValue = boolValue ? 1 : 0;
Furthermore, when bool values are inserted into streams then true is represented by 1, and false is represented by 0. Consider the following example:
cout << "A true value: " << true << "\n"
"A false value: " << false << '\n';
The bool data type is found in other programming languages as well. Pascal has its type Boolean; Java has a boolean type. Different from these languages, C++'s type bool acts like a kind of int type. It is primarily a documentation-improving type, having just two values true and false. Actually, these values can be interpreted as enum values for 1 and 0. Doing so would ignore the philosophy behind the bool data type, but nevertheless: assigning true to an int variable neither produces warnings nor errors.
Using the bool-type is usually clearer than using int. Consider the following prototypes:
bool exists(char const *fileName); // (1)
int exists(char const *fileName); // (2)
With the first prototype, readers expect the function to return true if the given filename is the name of an existing file. However, with the second prototype some ambiguity arises: intuitively the return value 1 is appealing, as it allows constructions like
if (exists("myfile"))
cout << "myfile exists";
On the other hand, many system functions (like access, stat, and many other) return 0 to indicate a successful operation, reserving other values to indicate various types of errors.
As a rule of thumb I suggest the following: if a function should inform its caller about the success or failure of its task, let the function return a bool value. If the function should return success or various types of errors, let the function return enum values, documenting the situation by its various symbolic constants. Only when the function returns a conceptually meaningful integral value (like the sum of two int values), let the function return an int value.
3.4.2: The data type wchar_t
The wchar_t type is an extension of the char built-in type, to accommodate wide character values (but see also the next section). The g++ compiler reports sizeof(wchar_t) as 4, which easily accommodates all 65,536 different Unicode character values.
Note that Java's char data type is somewhat comparable to C++'s wchar_t type. Java's char type is 2 bytes wide, though. On the other hand, Java's byte data type is comparable to C++'s char type: one byte. Confusing?
3.4.3: Unicode encoding
In C++ string literals can be defined as NTBSs. Prepending an NTBS by L (e.g., L"hello") defines a wchar_t string literal.
C++ also supports 8, 16 and 32 bit Unicode encoded strings. Furthermore, two new data types are introduced: char16_t and char32_t storing, respectively, a UTF-16 and a UTF-32 unicode value.
A char type value fits in a utf_8 unicode value. For character sets exceeding 256 different values wider types (like char16_t or char32_t) should be used.
String literals for the various types of unicode encodings (and associated variables) can be defined as follows:
char utf_8[] = u8"This is UTF-8 encoded.";
char16_t utf16[] = u"This is UTF-16 encoded.";
char32_t utf32[] = U"This is UTF-32 encoded.";
Alternatively, unicode constants may be defined using the \u escape sequence, followed by a hexadecimal value. Depending on the type of the unicode variable (or constant) a UTF-8, UTF-16 or UTF-32 value is used. E.g.,
char utf_8[] = u8"\u2018";
char16_t utf16[] = u"\u2018";
char32_t utf32[] = U"\u2018";
Unicode strings can be delimited by double quotes but raw string literals can also be used.
3.4.4: The data type long long int
C++ also supports the type long long int. On 32 bit systems it has at least 64 usable bits.
3.4.5: The data type size_t
The size_t type is not really a built-in primitive data type, but a data type that is promoted by POSIX as a typename to be used for non-negative integral values answering questions like how much and how many, in which case it should be used instead of unsigned int. It is not a specific C++ type, but also available in, e.g., C. Usually it is defined implicitly when a (any) system header file is included. The header file officially defining size_t in the context of C++ is cstddef.
Using size_t has the advantage of being a conceptual type, rather than a standard type that is then modified by a modifier. Thus, it improves the self-documenting value of source code.
Several suffixes can be used to expicitly specify the intended representation of integral constants, like 42UL defining 42 as an unsigned long int. Likewise, suffixes uz or zu can be used to specify that an integral constant is represented as a size_t, as in: cout << 42uz.
Sometimes functions explictly require unsigned int to be used. E.g., on amd-architectures the X-windows function XQueryPointer explicitly requires a pointer to an unsigned int variable as one of its arguments. In such situations a pointer to a size_t variable can't be used, but the address of an unsigned int must be provided. Such situations are exceptional, though.
Other useful bit-represented types also exists. E.g., uint32_t is guaranteed to hold 32-bits unsigned values. Analogously, int32_t holds 32-bits signed values. Corresponding types exist for 8, 16 and 64 bits values. These types are defined in the header file cstdint and can be very useful when you need to specify or use integral value types of fixed sizes.
3.4.6: The data type std::byte
Quite often 8-bit variables are required, usually to access memory locations. Traditionally the char type has been used for that, but char is a signed type and when inserting a char variable into a stream the character's representation instead of its value is used. Maybe more important is the inherent confusion when using char type variables when only using its (unsigned) value: a char documents to the reader that text is used instead of mere 8-bit values, as used by the smallest addressable memory locations.
Different from the char type the std::byte type intends to merely represent an 8-bit value. In order to use std::byte the <cstddef> header file must be included.
The byte is defined as a strongly typed enum, simply embedding an unsigned char:
enum class byte: unsigned char
{};
As a byte is an enum without predefined enum values plain assignments can only be used between byte values. Byte variables can be initialized using curly brackets around an existing byte or around fixed values of at most 8 bits (see #1 in the following example). If the specified value doesn't fit in 8 bits (#2) or if the specified value is neither a byte nor an unsigned char type variable (#3) the compiler reports an error.
Assignments or assignment-like initializations using rvalues which are bytes initialized using parentheses with values not fitting in 8 bits are accepted (#4, #5). In these cases, the specified values are truncated to their lowest 8 bits. Here are the illustrations:
byte value{ 0x23 }; // #1 (see the text above)
// byte error{ 0x123 }; // #2
char ch = 0xfb;
// byte error{ ch }; // #3
byte b1 = byte( ch ); // #4
value = byte( 0x123 ); // #5
The byte type supports all bit-wise operations, but the right-hand operand of the bit-wise operator must also be a byte. E.g.,
value &= byte(0xf0);
Byte type values can also be ordered and compared for (in)equality.
Unfortunately, no other operations are supported. E.g., bytes cannot be added and cannot be inserted into or extracted from streams, which somehow renders the std::byte less useful than ordinary types (like unsigned int, uint16_t). When needed such operations can be supported using casts (covered in section [3.5]({{< relref "/docs/A First Impression/#35-a-new-syntax-for-casts" >}})), but it's considered good practice to avoid casts whenever possible. However, C++ allows us to define a byte-type that does behave like an ordinary numeric type, including and extracting its values into and from streams. In section 11.4 such a type is developed.
3.4.7: Digit separators
To improve the readability of large numbers digit separators for integer and floating point literals can be used. The digit separator is a single quote which may be inserted between digits of such literals to enhance human readability. Multiple digit separators may be used, but only one separator can be inserted between successive digits. E.g.,
1'000'000
3.141'592'653'589'793'238'5
''123 // won't compile
1''23 // won't compile either
3.5: A new syntax for casts
Traditionally, C offers the following cast syntax:
(typename)expression
here typename is the name of a valid type, and expression is an expression.
C style casts are now deprecated. C++ programs should merely use the new style C++ casts as they offer the compiler facilities to verify the sensibility of the cast. Facilities which are not offered by the classic C-style cast.
A cast should not be confused with the often used constructor notation:
typename(expression)
the constructor notation is not a cast, but a request to the compiler to construct an (anonymous) variable of type typename from expression.
If casts are really necessary one of several new-style casts should be used. These new-style casts are introduced in the upcoming sections.
3.5.1: The static_cast operator
The static_cast<type>(expression) is used to convert conceptually comparable or related types to each other. Here as well as in other C++ style casts type is the type to which the type of expression should be cast.
Here are some examples of situations where the static_cast can (or should) be used:
-
When converting an int to a double.
This happens, for example when the quotient of two int values must be computed without losing the fraction part of the division. The sqrt function called in the following fragment returns 2:
int x = 19; int y = 4; sqrt(x / y); -
whereas it returns 2.179 when a
static_castis used, as in:sqrt(static_cast<double>(x) / y); -
The important point to notice here is that a
static_castis allowed to change the representation of its expression into the representation that's used by the destination type. -
Also note that the division is put outside of the cast expression. If the division is performed within the cast's expression (as in
static_cast<double>(x / y)) an integer division has already been performed before the cast has had a chance to convert the type of an operand to double. -
When converting enum values to int values (in any direction).
Here the two types use identical representations, but different semantics. Assigning an ordinary enum value to an int doesn't require a cast, but when the enum is a strongly typed enum a cast is required. Conversely, a static_cast is required when assigning an int value to a variable of some enum type. Here is an example:
enum class Enum { VALUE }; cout << static_cast<int>(Enum::VALUE); // show the numeric value -
When converting related pointers to each other.
The
static_castis used in the context of class inheritance (cf. chapter 13) to convert a pointer to a so-calledderived classto a pointer to its base class. It cannot be used for casting unrelated types to each other (e.g., astatic_castcannot be used to cast a pointer to a short to a pointer to an int).A
void *is a generic pointer. It is frequently used by functions in the C library (e.g.,memcpy(3)). Since it is the generic pointer it is related to any other pointer, and astatic_castshould be used to convert avoid *to an intended destination pointer. This is a somewhat awkward left-over from C, which should probably only be used in that context. Here is an example:The
qsortfunction from the C library expects a pointer to a (comparison) function having twovoid const *parameters. In fact, these parameters point to data elements of the array to be sorted, and so the comparison function must cast thevoid const *parameters to pointers to the elements of the array to be sorted. So, if the array is an int array[] and the compare function's parameters arevoid const *p1andvoid const *p2then the compare function obtains the address of the int pointed to byp1by using:static_cast<int const *>(p1); -
When undoing or introducing the signed-modifier of an int-typed variable (remember that a
static_castis allowed to change the expression's representation!).Here is an example: the C function tolower requires an int representing the value of an unsigned char. But char by default is a signed type. To call tolower using an available char ch we should use:
tolower(static_cast<unsigned char>(ch))
3.5.2: The const_cast operator
The const keyword has been given a special place in casting. Normally anything const is const for a good reason. Nonetheless situations may be encountered where the const can be ignored. For these special situations the const_cast should be used. Its syntax is:
const_cast<type>(expression)
A const_cast<type>(expression) expression is used to undo the const attribute of a (pointer) type.
The need for a const_cast may occur in combination with functions from the standard C library which traditionally weren't always as const-aware as they should. A function strfun(char *s) might be available, performing some operation on itschar *s parameter without actually modifying the characters pointed to by s. Passing char const hello[] = "hello"; to strfun produces the warning
passing `const char *' as argument 1 of `fun(char *)' discards const
A const_cast is the appropriate way to prevent the warning:
strfun(const_cast<char *>(hello));
3.5.3: The reinterpret_cast operator
The third new-style cast is used to change the interpretation of information: the reinterpret_cast. It is somewhat reminiscent of the static_cast, but reinterpret_cast should only be used when it is known that the information as defined in fact is or can be interpreted as something completely different. Its syntax is:
reinterpret_cast<pointer type>(pointer expression)
Think of the reinterpret_cast as a cast offering a poor-man's union: the same memory location may be interpreted in completely different ways.
The reinterpret_cast is used, for example, in combination with the write function that is available for streams. In C++ streams are the preferred interface to, e.g., disk-files. The standard streams like std::cin and std::cout also are stream objects.
Streams intended for writing (output streams like cout) offer write members having the prototype
write(char const *buffer, int length)
To write the value stored within a double variable to a stream in its un-interpreted binary form the stream's write member is used. However, as a double * and a char * point to variables using different and unrelated representations, a static_cast cannot be used. In this case a reinterpret_cast is required. To write the raw bytes of a variable double value to cout we use:
cout.write(reinterpret_cast<char const *>(&value), sizeof(double));
All casts are potentially dangerous, but the reinterpret_cast is the most dangerous of them all. Effectively we tell the compiler: back off, we know what we're doing, so stop fuzzing. All bets are off, and we'd better do know what we're doing in situations like these. As a case in point consider the following code:
int value = 0x12345678; // assume a 32-bits int
cout << "Value's first byte has value: " << hex <<
static_cast<int>(
*reinterpret_cast<unsigned char *>(&value)
);
The above code produces different results on little and big endian computers. Little endian computers show the value 78, big endian computers the value 12. Also note that the different representations used by little and big endian computers renders the previous example (cout.write(...)) non-portable over computers of different architectures.
As a rule of thumb: if circumstances arise in which casts have to be used, clearly document the reasons for their use in your code, making double sure that the cast does not eventually cause a program to misbehave. Also: avoid reinterpret_casts unless you have to use them.
3.5.4: The dynamic_cast operator
Finally there is a new style cast that is used in combination with polymorphism (see chapter 14). Its syntax is:
dynamic_cast<type>(expression)
Different from the static_cast, whose actions are completely determined compile-time, the dynamic_cast's actions are determined run-time to convert a pointer to an object of some class (e.g., Base) to a pointer to an object of another class (e.g., Derived) which is found further down its so-called class hierarchy (this is also called downcasting).
At this point in the Annotations a dynamic_cast cannot yet be discussed extensively, but we return to this topic in section 14.6.1.
3.5.5: Casting shared_ptr objects
This section can safely be skipped without loss of continuity.
In the context of the class shared_ptr, which is covered in section 18.4, several more new-style casts are available. Actual coverage of these specialized casts is postponed until section 18.4.5.
These specialized casts are:
- static_pointer_cast, returning a
shared_ptrto thebase-classsection of aderived classobject; - const_pointer_cast, returning a
shared_ptrto a non-const object from ashared_ptrto a constant object; - dynamic_pointer_cast, returning a
shared_ptrto aderived classobject from ashared_ptrto a base class object.
3.6: Keywords and reserved names in C++
C++'s keywords are a superset of C's keywords. Here is a list of all keywords of the language:
alignas char16_t double long reinterpret_cast true
alignof char32_t dynamic_cast module requires try
and class else mutable return typedef
and_eq co_await enum namespace short typeid
asm co_return explicit new signed typename
atomic_cancel co_yield export noexcept sizeof union
atomic_commit compl extern not static unsigned
atomic_noexcept concept false not_eq static_assert using
auto const float nullptr static_cast virtual
bitand const_cast for operator struct void
bitor constexpr friend or switch volatile
bool continue goto or_eq synchronized wchar_t
break decltype if private template while
case default import protected this xor
catch delete inline public thread_local xor_eq
char do int register throw
Notes:
-
Since the C++17 standard the keyword
registeris no longer used, but it remains a reserved identifier. In other words, definitions likeregister int index;result in compilation errors. Also,
registeris no longer considered a storage class specifier (storage class specifiers areextern,thread_local,mutableandstatic). -
the operator keywords:
and,and_eq,bitand,bitor,compl,not,not_eq,or,or_eq,xorandxor_eqare symbolic alternatives for, respectively,&&,&=,&,|,~,!,!=,||,|=,^and^=. -
C++ also recognizes the special identifiers final, override, transaction_safe, and transaction_safe_override. These identifiers are special in the sense that they acquire special meanings when declaring classes or polymorphic functions. Section 14.4 provides further details.
Keywords can only be used for their intended purpose and cannot be used as names for other entities (e.g., variables, functions, class-names, etc.). In addition to keywords identifiers starting with an underscore and living in the global namespace (i.e., not using any explicit namespace or using the mere :: namespace specification) or living in the std namespace are reserved identifiers in the sense that their use is a prerogative of the implementor.